Chapter Nineteen: Metabolic Acidosis, part 2
References
Chapter 19, Part 2 July 13, 2023
Roger mentioned MELAS syndrome MELAS syndrome: Clinical manifestations, pathogenesis, and treatment options
Josh mentioned this blog on lactate- Understanding lactate in sepsis & Using it to our advantage
We discussed the Warburg effect The Warburg Effect: How Does it Benefit Cancer Cells? - PMC and here’s a case from skeleton key- Skeleton Key Group Case #28: Mysterious Acidosis in Cancer - Renal Fellow Network
Otto Warburg won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1931 for describing how animal tumors produce large quantities of lactic acid (Wikipedia)
Joel calls it the Lactate saline reflex, but the accepted term of art is Lacto-Bolo reflex The origins of the Lacto-Bolo reflex: the mythology of lactate in sepsis
Buffer agents do not reverse intramyocardial acidosis during cardiac resuscitation.
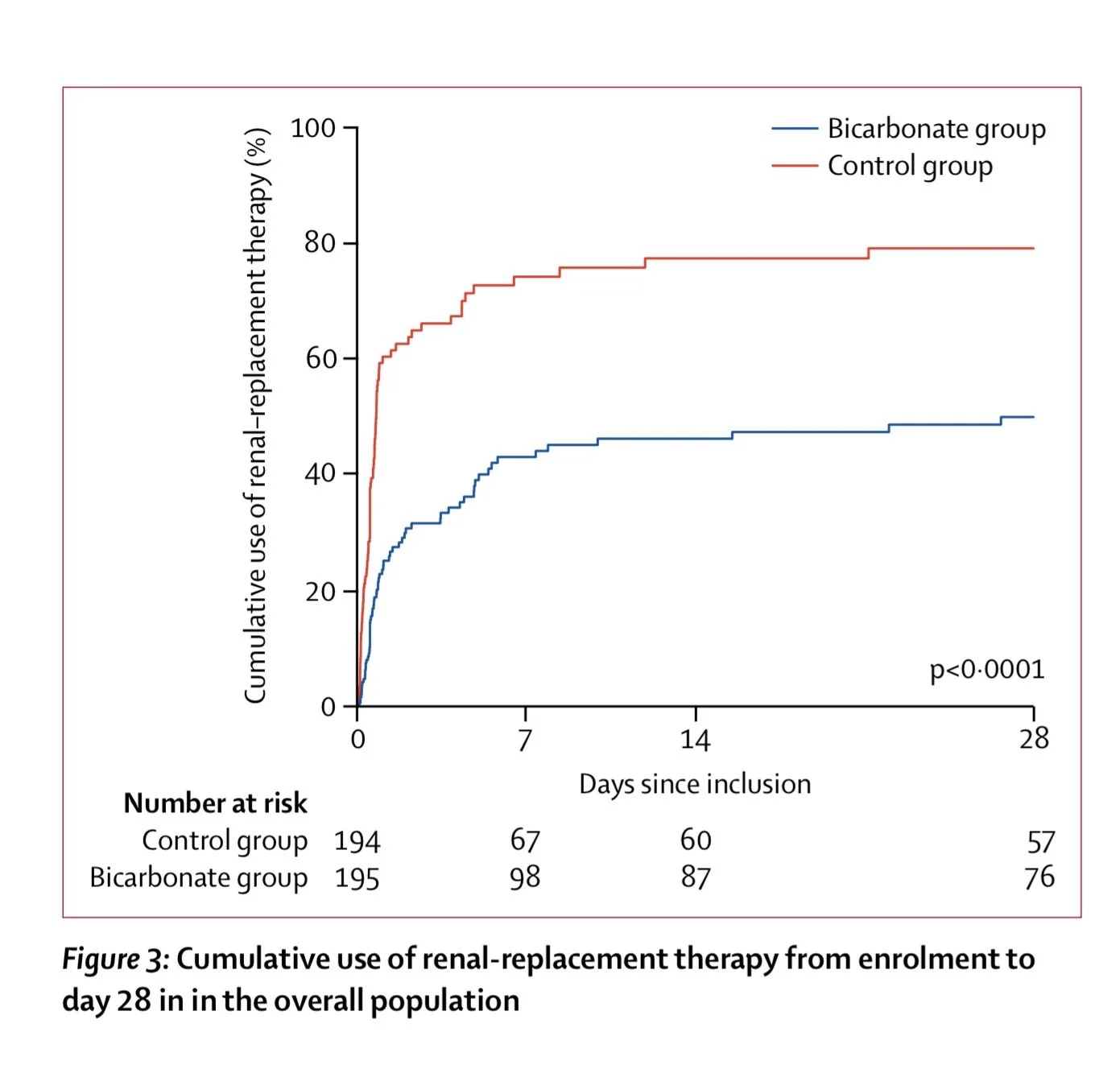
Josh mentioned this article the BICAR-ICU Sodium bicarbonate therapy for patients with severe metabolic acidaemia in the intensive care unit (BICAR-ICU): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled, phase 3 trial - The Lancet
Roger shared 3 quotes to make the point that there has been little movement in our knowledge the past 40 years:
Bicarbonate does not improve hemodynamics in critically ill patients who have lactic acidosis. A prospective, controlled clinical study from Cooper in the Annals
Lactic Acidosis and Bicarbonate Therapy | Annals of Internal Medicine from Robert Hollander
Lactic acidosis from Nick Madias
Josh mentioned the use of sodium bicarbonate for CKD Eubicarbonatemic Hydrogen Ion Retention and CKD Progression - Kidney Medicine (Madias) Bicarbonate therapy for prevention of chronic kidney disease progression (from Wesson), Sodium Bicarbonate Prescription and Extracellular Volume Increase: Real‐world Data Results from the AlcalUN Study
Amy’s VoG on metabolic acidosis/KDIGO guidelines
Very nice JASN review that describes the mechanisms of how metabolic acidosis leads to CKD progression
1930 Lancet description of benefit
2009 RCT that the 2012 KDIGO guidelines sort of based their 2b recommendations off of
We discussed methanol toxicity : Case Study: Methanol Poisoning from Adulterated Liquor | Food Safety, Acute methyl alcohol poisoning: a review based on experiences in an outbreak of 323 cases and josh poking at the osmolar gap: PulmCrit- Toxicology dogmalysis: the osmolal gap and shared these guidelines: METHANOL | extrip-workgroup and Roger loves this: Urine fluorescence using a Wood's lamp to detect the antifreeze additive sodium fluorescein: a qualitative adjunctive test in suspected ethylene glycol ingestions
From China to Panama, a Trail of Poisoned Medicine - The New York Times (diethylene glycol) . The Accidental Poison That Founded the Modern FDA - The Atlantic
Outline: Chapter 19 Metabolic Acidosis
Etiologies and Diagnosis
Lactic Acidosis
Pyruvate → lactate (LDH; NADH → NAD+)
Normal production: 15–20 mmol/kg/day
Metabolized in liver/kidney → pyruvate → glucose or TCA
Normal lactate: 0.5–1.5 mmol/L; acidosis if > 4–5 mmol/L
Causes:
↑ production: hypoxia, redox imbalance, seizures, exercise
↓ utilization: shock, hepatic hypoperfusion
Malignancy, alcoholism, antiretrovirals
D-lactic acidosis
Short bowel/jejunal bypass
Glucose → D-lactate (not metabolized by LDH)
Symptoms: confusion, ataxia, slurred speech
Special assay needed
Tx: bicarb, oral antibiotics
Treatment
Underlying cause
Bicarb controversial: may worsen intracellular acidosis, overshoot alkalosis, ↑ lactate
Target pH > 7.1; prefer mixed venous pH/pCO2
Ketoacidosis (Chapter 25 elaborates)
FFA → TG, CO2, H2O, ketones (acetoacetate, BHB)
Requires:
↑ lipolysis (↓ insulin)
Hepatic preference for ketogenesis
Causes:
DKA (glucose > 400)
Fasting ketosis (mild)
Alcoholic ketoacidosis
Poor intake + EtOH → ↓ gluconeogenesis, ↑ lipolysis
Mixed acid-base (vomiting, hepatic failure, NAGMA)
Congenital organic acidemias, salicylates
Diagnosis:
AG, osmolar gap (acetone, glycerol)
Ketones: nitroprusside only detects acetone/acetoacetate
BHB can be 90% of total (false negative)
Captopril → false positive
Treatment:
Insulin +/- glucose
Renal Failure
↓ excretion of daily acid load
GFR < 40–50 → ↓ ammonium/TA excretion
Bone buffering stabilizes HCO3 at 12–20 mEq/L
Secondary hyperparathyroidism helps with phosphate buffering
Alkali therapy controversial in adults
Ingestions
Salicylates
Symptoms at >40–50 mg/dL
Early: respiratory alkalosis → Later: metabolic acidosis
Treatment: bicarb, dialysis (>80 mg/dL or coma)
Methanol
Metabolized to formic acid → retinal toxicity
Osmolar gap elevated
Tx: bicarb, ethanol/fomepizole, dialysis
Ethylene glycol
→ glycolic/oxalic acid → renal failure
Same treatment + thiamine/pyridoxine
Other
Toluene, sulfur, chlorine gas, hyperalimentation (arginine, lysine)
GI Bicarbonate Loss
Diarrhea, bile/pancreatic drainage → loss of alkaline fluids
Ureterosigmoidostomy → Cl-/HCO3- exchange in colon
Cholestyramine → Cl- for HCO3-